top of page

Elimination
Organic
AS
Alcohols
AQA Content
Outline the mechanism for the elimination of water from alcohols.
Specification Notes
Alkenes can be formed from alcohols by acid-catalysed elimination reactions.
Alkenes produced by this method can be used to produce addition polymers without using monomers derived from crude oil.
Notes
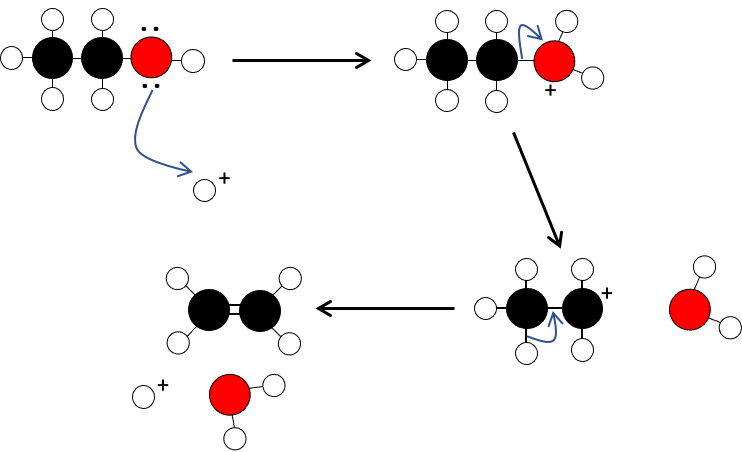
Dehydration: The formation of alkenes by the removal of water
An alcohol is converted into an alkene by dehydration in the presence of an acid and heat.
The reaction is catalysed by an acid (sulfuric or phosphoric) at high temperature (160°C).
For ethanol:
1. The alcohol is protonated
2. The carbon-oxygen bond undergoes heterolysis
3. The water leaves forming a carbocation
4. The carbocation loses hydrogen to the conjugate base of the acid to form an alkene and the reformed acid
Links
bottom of page